Sugar and excessive fructose corn syrup are the unique industrial sweeteners—cheap, crammed with empty energy, and contributing to illnesses resembling weight problems, kind 2 diabetes, cavities, and metabolic syndrome. Synthetic sweeteners, like NutraSweet, Splenda, and Candy’N Low, are the second-generation sweeteners. They’re virtually calorie-free, however cautions have been raised about their antagonistic results. Sugar alcohols, resembling sorbitol, xylitol, and erythritol, are the third-generation sweeteners. They’re low in energy however carry laxative results or even worse. What about uncommon sugars like allulose?
What Is Allulose?
Allulose is a pure, so-called uncommon sugar, current in restricted portions in nature. “Latest technological advances, resembling enzymatic engineering utilizing genetically modified microorganisms, now enable [manufacturers] to supply in any other case uncommon sugars” like allulose in substantial portions.
Allulose and Weight Loss
What occurred when researchers evaluated the impact of allulose on fats mass discount in folks? As I focus on in my video Is Allulose a Wholesome Sweetener?, greater than 100 people had been randomized to a placebo management (0.012 grams of sucralose twice a day), a teaspoon (4 g) of allulose twice a day, or 1¾ teaspoons (7 g) of allulose twice a day for 12 weeks. Regardless of no modifications in bodily exercise or calorie consumption within the teams, physique fats considerably decreased following allulose supplementation. There weren’t any vital modifications in LDL levels of cholesterol in both of the allulose teams, although.
What in regards to the purported anti-diabetes results?
Does Allulose Assist with Diabetes?
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover experiment, folks with borderline diabetes consumed a cup of tea containing both 1¼ teaspoons (5 g) of allulose or no allulose (management) with a meal. There was a major discount in blood sugar ranges 30 and 60 minutes after consumption, however it was solely about 15% decrease in comparison with the management group and didn’t final past the primary hour. To check long-term security, the identical researchers then randomized wholesome folks to a bit of over a teaspoon (5 g) of allulose 3 times a day with meals for 12 weeks. There didn’t look like any antagonistic unintended effects, however there weren’t any results on weight or blood sugar ranges both. So, it seems the physique fats information are blended, as are the sugar information.
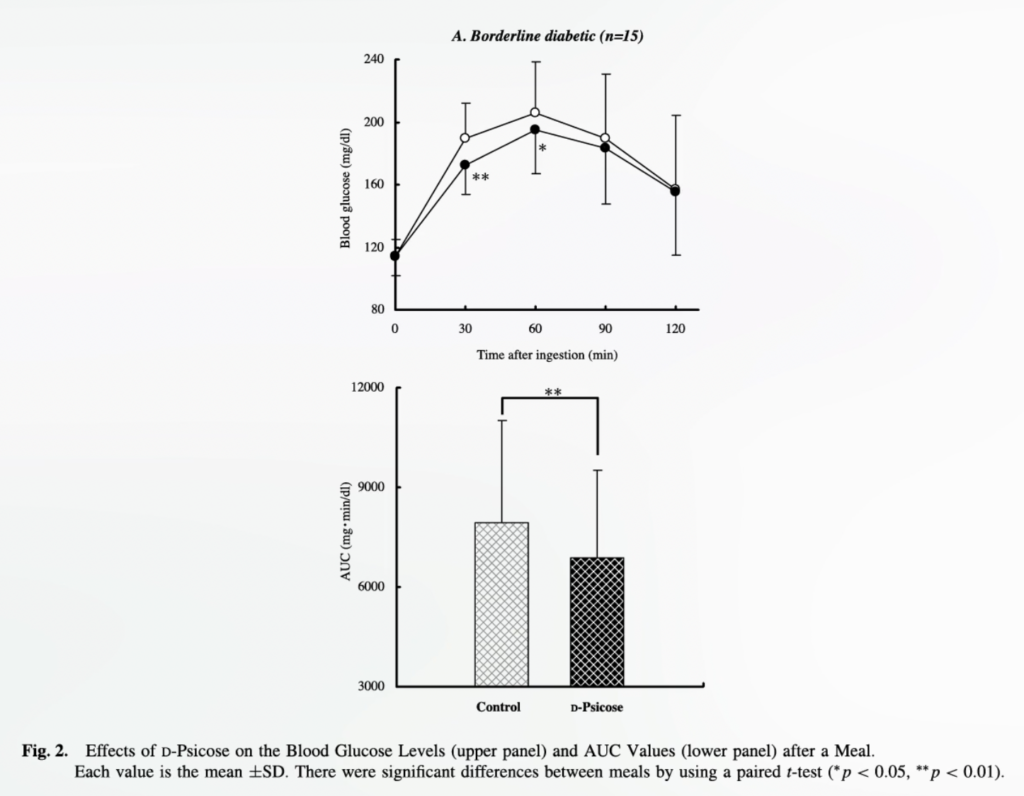
One other examine discovered no results of allulose on blood sugar ranges in wholesome members examined as much as two hours after consumption, although an identical examine on people with diabetes did. And a scientific overview and meta-analysis of all such managed feeding trials prompt that the acute profit on blood sugars was of “borderline significance.” It’s unclear whether or not this small and apparently inconsistent impact might translate into significant enhancements in long-term blood sugar management. It is probably not sufficient simply so as to add allulose—you may additionally have to chop out junk meals.
Is Allulose Good or Unhealthy for You?
As I focus on in my video Does the Sweetener Allulose Have Aspect Results?, not like desk sugar, allulose is protected for our enamel; it apparently isn’t metabolized by cavity-causing micro organism to supply acid and promote plaque buildup. It doesn’t elevate blood sugar ranges both, even in folks with diabetes. Allulose is thought-about a “comparatively unhazardous” sugar, however what does that imply?
How A lot Allulose Is Too A lot?
In a single examine, researchers gave wholesome adults drinks containing steadily larger doses of allulose “to establish the utmost single dose for infrequent ingestion.” No circumstances of extreme gastrointestinal signs had been famous till a dose of 0.4 g per kg of body weight was reached, which is about eight teaspoons for the common American. Extreme signs of diarrhea had been famous at a dose of 0.5 g per kg of body weight, or about ten teaspoons.
When it comes to a day by day higher restrict given in smaller doses all through the day, as soon as members reached round 17 teaspoons (1.0 g/kg body weight) a day, relying on weight, some skilled extreme nausea, stomach ache, headache, or diarrhea. So, most adults in the US ought to in all probability keep beneath single doses of about 8 teaspoons (0.4 g per kg of body weight) and never exceed about 18 teaspoons (0.9 g per kg of body weight) for the entire day.
So, What’s the Verdict on Allulose?
Are uncommon sugars like allulose a wholesome different for conventional sweeteners? Effectively, contemplating the number of doubtlessly useful results of allulose “with out recognized disadvantages from metabolic and toxicological research, allulose might presently be probably the most promising uncommon sugar.” However how a lot is that saying? We simply don’t have a number of good human information. “On account of the absence of those research, it could be too early to advocate uncommon sugars for human consumption.” That is very true given the erythritol debacle.



